Differences between olive extracts.
Which is the difference between olive fruit and olive leaf extract? How much different are Hydroxytyrosol and Oleuropein? Do they have the same applications? Can we use the same dose for both of them?
These are some of the usual questions asked by our clients interested in olive extracts. It is logical. Because even if people know that this plant is very healthy, the benefits differ according to the part of the olive tree. Olive fruit and olive leaf contain different concentrations of actives, and it happens the same between the fruit and the olive seed.
In this article we clear up the doubts regarding olive extracts so that you can choose the best solution for your needs.
Let’s start!
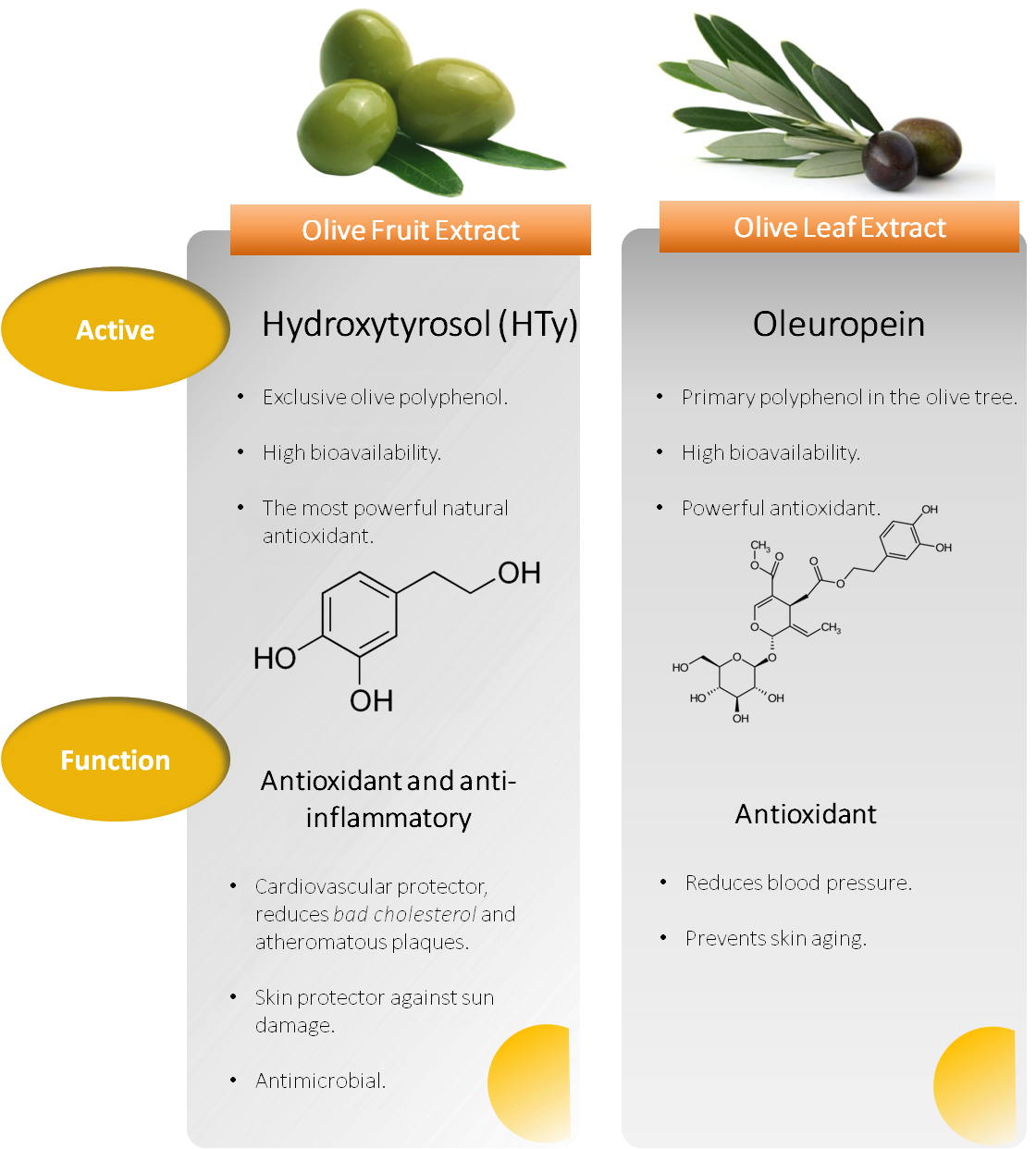


All HT functions in this article.

In Nutexa we submit the ingredients to a minimally invasive process that respects the environment. Each product requires a different treatment. In general, HT extracts involve a long and complex process, while those of Oleuropein are more standard, with shorter times.

The solubility in water, alcohols and oils varies according to the percentage and the format.
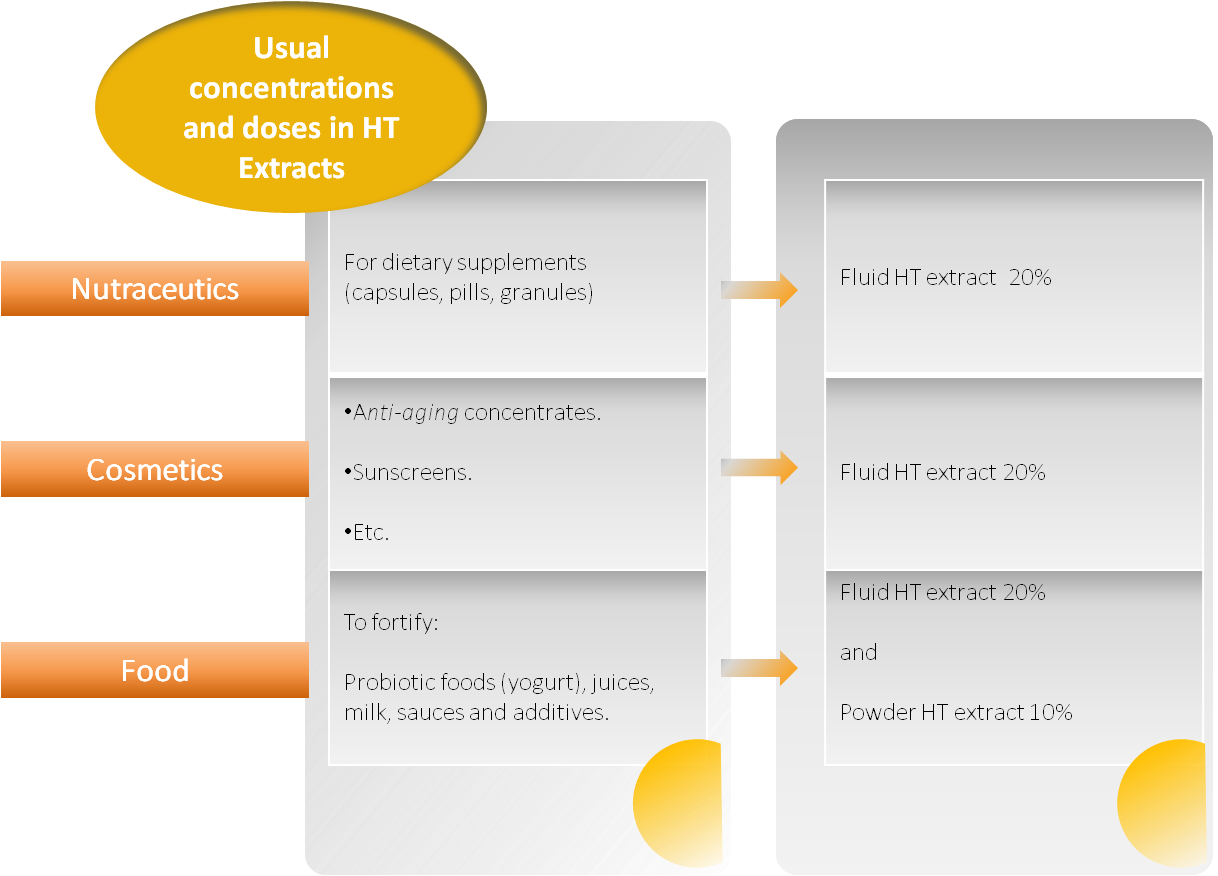
Scientific support
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)’s panel of experts declared in 2011 that the daily consumption of 5 mg of Hydroxytyrosol contributes to the prevention of LDL oxidation.
At the same time, it granted to Olive Fruit extract a health claim authorizing the products that include this type of extract to publicize its cardiovascular benefits.
On the other hand, it is the only natural substance in EFSA’s antioxidants list that does not come from a vitamin or mineral.
EFSA’s recognition of olive polyphenols also reaches other products such as Oleuropein extracts.
Common advantages
- They are of natural origin.
- They are purified.
- They allow to provide the necessary dose to minimize the appearance of certain diseases.
- Their effectiveness is scientifically proven and supported by the EFSA.
If you have other questions or want more information about olive extracts, contact us.
SCIENTIFIC REFERENCES
- Elisa Tripoli et al. The phenolic compounds of olive oil: structure, biological activity and beneficial effects on human health. Nutr Res Rev 2005;18:98-112.
- Minor Components of Olive Oil: Evidence to Date of Health Benefits in Humans. Covas, M.I., Visioli, F. et al. Nutrition Reviews, Vol. 64, No. 9
- Raederstorff, D., Antioxidant activity of olive polyphenols in humans: a review. Int. J. Vitam Nutr. Res. 2009, 79, 152– 165.
- Castañer O, Covas MI, Khymenets O, Nyyssonen K, Konstantinidou V, Zunft HF, de la Torre R, Muñoz-Aguayo D, Vila J, Fitó M. Protection of LDL from oxidation by olive oil polyphenols is associated with a downregulation of CD40-ligand expression and its downstream products in vivo in humans. American Journal of Clin Nutr. 2012 May; 95(5):1238-44.
- Lipoproteínas de baja densidad oixdadas. Rev Electron Biomed / Electron J Biomed 2008;3:52-60.- Calmarza, P.
- N El, S., Karakaya, S. 2009. Olive tree (Olea europaea) leaves: potencial .
- Perrinjaquet-Moccetti, T., Busjahn, A., Schmidlin, C., Schmidt, A.,Bradl, B., Aydogan, C. 2008. Food supplementation with an olive (Olea europaea L.) leaf extract reduces blood pressure in borderline hypertensive monozygotic twins. Phytotherapy Research, 22:1239-1242.
- Hwan Lee, O., Yong Lee, B. 2010. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of individual and combined phenolics in Olea europaea leaf extract. Bioresource Technology, 101:3751-3754.





