
The olive tree, essential in the revolution of sunscreens.
Hydroxytyrosol, the most powerful antioxidant in the olive and practically of all the vegetable kingdom, is revealed as an indispensable product in the formulation of sunscreens. Due to its exclusive properties, it is the cosmetic ingredient with the greatest capacity to combat the sun damage on the skin.
As we explained in a previous article, the properties of Hydroxytyrosol (HTy) confers to this polyphenol – only present in the olive plant – to be one of the most effective antioxidants for the cosmetic industry.
Its high power to fight the oxidation of cells caused by free radicals in the body is very important, since cell degradation is the trigger of diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s, cardiovascular problems and the ageing of the skin.
Free radicals, on the other hand, originate from internal causes but also from external factors such as tobacco, alcohol, environmental pollution and solar radiation, the latter being one of the most aggressive due to its daily and inevitable impact in the human being.
Sunscreens should aim to protect the skin from the damage caused by the rays of sunlight – not to increase the duration of sun exposure. However, traditionally used filters are not capable of preventing the formation of free radicals. This forces the industry to seek new mechanisms for sun protection.
These new solutions go through the development of formulas that act in the deepest layers of the skin as well as the incorporation of antioxidants that can cope with the specific characteristics that occur in the oxidation process caused by solar radiation.
Hydroxytyrosol has not only demonstrated its ability to combat this process but also the fact that, nowadays, it is one of the few substances with the power to challenge the Sun.
This specific property of the HTy can be exploited in the industry of sunscreens and could suppose a change of concept in this type of cosmetic products.
In order to demonstrate the importance of including olive fruit extracts in solar cosmetics, it is necessary to explain how the radiation affects the skin and how it should be adequately protected.

Contenido del artículo
Why the rays of sunlight damage the skin?
The Sun emits energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation, which is popularly known as rays. This energy impacts on the objects that cross in its path and interacts inside all those it manages to cross. In the case of living beings, it can reach DNA and cause alterations in it.
The effects of the electromagnetic energy depen on the wavelength. Grosso modo, we could say that, the shorter the length, the greater the intensity of the energy on the object.
In the case of the Earth, the rays with the shortest wavelength – and therefore the most dangerous – stay out of the atmosphere and only those medium or long wavelengths can cross it: ultraviolet rays (UV) of type B (from 280 to 320 nm in length) and type A (320-400 nm); the visible rays (400 – 700 nm); and the infrared rays (IR), which range from 700 nm to 1 mm and are also classified as A, B and C, with the C being the least energetic. However, longer lengths do not mean they are innocuous, as they still contain energy.
Half of the solar radiation comes from infrared rays of type A (IR-A), 40% are visible rays, and only 10% comes from the ultraviolet, practically of the UV-A type (99%). However, UV-B has an impact on the skin since type A rays add to the former ones and enhance their effects.
Problem 1. Traditional sunscreens retain ultraviolet rays BUT have no effect on infrared rays, which have a greater impact on the skin. There are even formulas that only exert against UV-B rays.
The effects of each radiation vary according to their nature too. Visible light basically acts on the photosynthesis of plants. While the infrared rays B and C do not penetrate the human skin and their effects are only felt at a thermal level.
The skin damage of UV-A and UV-B
Broadly speaking, the visible and short-term effect of UV-A would be tanning and that of UV-B, the burn. But it is internally and long-term where the damage occurs. Specifically, in the first layer of the skin: the epidermis, which is the maximum point at which they arrive.
UV-B rays are associated with an increase of the activity and the number of melanocytes. This can cause a benign concentration, which manifests itself in the formation of freckles, moles and lentigines.
On the other hand, UV rays lead to several processes that can cause: cell death; the mutation of the cells (which can cause cancer); anti-oncogenic actions by some proteins; and an increase in free radicals. The latter leads to the oxidation of cells, which triggers a process that negatively affects the collagen and ends up causing premature aging, which results in wrinkles, spots, and thin skin, among other symptoms.
Problem 2. Sunscreens should include antioxidants to slow down the creation of free radicals. Nevertheless, traditional products ONLY absorb and / or reflect UV rays through chemical or physical filters.
The effect of chemical and physical filters is superficial and short-term. They only avoid or minimize sunburn and, at the same time, promote and maintain the tanning. However, continued exposure allows a part of the UV radiation to pass through the filter barrier and, consequently, to induce the creation of free radicals.
The skin damage of IR-A
The main characteristic of the type A infrared radiation – and the main difference from the ultraviolet radiation – is that it reaches the deepest layer of the skin: the hypodermis; and attacks the cellular mitochondria, responsible for the energy supply of the cell.
The process that takes place in the mitochondria is also very specific and should be known when formulating an effective sunscreen against this type of radiation.
According to in vitro and in vivo scientific studies, the arrival of the IR-A rays in the mitochondria causes an increase in free radicals of the ROS type (Reactive Oxygen Species). The accumulation of the latter causes an increase in the expression of MMP-1, a metalloproteinase involved in the degradation of dermal collagen. This leads, consequently, to the decomposition of the collagen itself, a protein that maintains the good condition of the skin, bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons and other parts of the human body.
In addition, we must add the fact that the impact of IR-A on the skin makes it difficult to create new collagen, which makes the picture worse.
It is worth mentioning that there are evidences that relate skin cancer to the genes involved in the response to stress and cell death caused by IR-A radiation, although this hypothesis still needs to be tested.
Problem 3. The sunscreens formulas must be able to protect the hypodermis, act in the mitochondria and stop the MMP-1 expression. A chemical and / or physical filter DOES NOT have the capacity to conduct this function.
The chemical filters used to protect the epidermis from UV radiation – based on synthetic chemicals – can not absorb the wavelength of infrared rays. Physical filters – inert inorganic powders that reflect the rays – also do not reach the hypodermis. And, in any case, none of them combats the damage caused by the IR in the mitochondria.
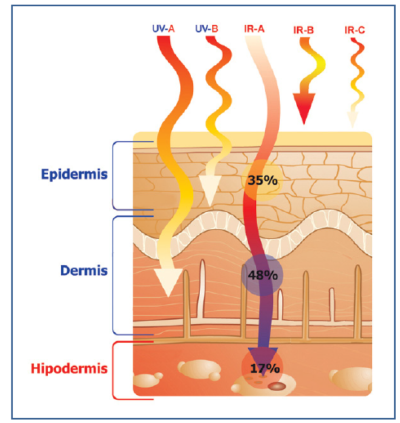
Scope of the waves coming from solar radiation on human skin. Source: Consejo General de Colegios Oficiales de Farmacéuticos de España.
Antioxidants, necessary in the protection against IR rays
The protection against IR-A radiation is of vital importance, not only because half of the rays come from it but also because of their ability to penetrate very deeply into human skin.
And here antioxidants play a fundamental role because, as we explained in this post, the best way to stop the oxidation of a molecule is through another one capable of avoiding this process. That is, that molecule that acts as an antioxidant agent.
Solution 1. Sunscreens must include antioxidants to stop the formation of free radicals from UV and IR radiation.
Biological filters, that is to say, those that contain antioxidants, act from the inside of the organism, unlike the chemical and physical ones. Although all together provide a total sun protection. The biological filters can also be supplemented with the oral intake of antioxidant supplements.
The importance of Hydroxytyrosol in sunscreens
Natural antioxidants are found mostly in plants; and there are various types according to their structure. This causes that some of them are more powerful than others and, therefore, react better in certain situations.
This is what happens in the relationship between antioxidants and sunscreens. As the investigations made until now prove, not all antioxidants can act against intramitochondrial ROS nor are they capable of inhibiting the increase of MMP-1 expression.
This is the case, for example, of vitamin E. In vivo studies have shown its poor effectiveness in reducing the increase of this metalloproteinase after the exposure to IR-A rays.
How does Hydroxytyrosol work instead? The most powerful polyphenol in the olive tree in terms of antioxidants is also superior to the rest of plant actives when it comes to capturing cells with loose electrons (free radicals, peroxides, etc.).
Read more about the properties of Hydroxytyrosol.
HTy is capable of reversing premature aging and dehydration of the skin. But according to the extensive scientific literature, we can also affirm its ability to combat photo-aging (the one caused by solar radiation).
On the one side, numerous studies prove the effectiveness of HTy extract on free radicals caused by UV-A rays. On the other hand, there are signs to its power to reduce significantly the breakage of the DNA chains caused by UV-B radiation.
And the most important evidence: extracts of HTy are able to stop the production of MMP-1 triggered by ultraviolet rays. Moreover, in studies in which its reaction has been compared with that of other substances, Hydroxytyrosol has been the only one to be able to reduce the increase in this expression.
In addition, the effects of olive fruit extracts reach the cellular mitochondria. Numerous international studies prove the relationship between HTY and the improvement in the functioning of mitochondrias and in the reduction of the damage that occurs in them.
Solution 2. Hydroxytyrosol extracts reduce the increase in MMP-1 that caused by solar radiation and act in the mitochondria, both key points when it comes to protecting the skin from the sun.
Related articles:
The value of antioxidants in cosmestics.
Hydroxytyrosol, the superhero of cosmetic antioxidants.
If you want to incorporate olive fruit extracts to your products, contact us for more information and advice.
SCIENTIFIC REFERENCES:
- Lim HW, Cooper K. The health impact of solar radiation and prevention strategies: rapport of the Environment Council, American Academy of Dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol 1999; 41: 81-99.
- Trullàs C, Coll J, Del Río R, Lecha M, Pelejero C. Evaluating the IR photoprotection factor of physical sunscreens by bioengineering methods. 18th International I.F.S.C.C. Congress. Venecia, 1994; 1: 73-81.
- Philip Ludwig, Laura Szymczak. High Purity Hydroxytyrosol Protects Skin Cells from Environmental Stressors and Increases in-vitro Cell Viability. Lonza (one of the world’s leading suppliers to the pharmaceutical, biotech and specialty ingredients markets).
- Guo W, An Y, Jiang L, Geng C, Zhong L. The protective effects of hydroxytyrosol against UVB-induced DNA damage in HaCaT cells. Phytotherapy research: PTR. 2010;24(3):352–9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2943 . [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Hao, J.; Shen, W.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Sharman, E.; Wang, Y.; Wertz, K.; et al. Hydroxytyrosol protects against oxidative damage by simultaneous activation of mitochondrial biogenesis and phase II detoxifying enzyme systems in retinal pigment epithelial cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 1089–1098.
- Cao, K.; Xu, J.; Zou, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, A.; Li, H.; Szeto, I.M.Y.; Shi, Y.; Long, J.; et al. Hydroxytyrosol prevents diet-induced metabolic syndrome and attenuates mitochondrial abnormalities in obese mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med.2014, 67, 396–407.
- Hao, J.; Shen, W.; Yu, G.; Jia, H.; Li, X.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Weber, P.; Wertz, K.; Sharman, E.; et al. Hydroxytyrosol promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial function in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 634–644.
- Philip Ludwig, Laura Szymczak. High Purity Hydroxytyrosol Protects Skin Cells from Environmental Stressors and Increases in-vitro Cell Viability. Lonza (one of the world’s leading suppliers to the pharmaceutical, biotech and specialty ingredients markets).
- Curso de fotoprotección del Consejo General de Colegios Oficiales de Farmacéuticos de España.




